Curious about the names given to male rabbits? They are commonly referred to as ‘bucks’. This straightforward term has significant implications, especially in breeding contexts. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of rabbit terminology, anatomy, behavior, reproduction, and care – providing insights for enthusiasts and owners alike, answering the question: what are male rabbits called?
Key Takeaways
- Male rabbits are called bucks, females are “does”, and their babies are known as kits or kittens
- bucks have about seven years of breeding capability, while does start from 5-6 months of age.
- Rabbits have lightweight skeletons, and continuously growing teeth, and their large ears help regulate body temperature; they also have powerful hind legs that aid in speed and agility.
- Rabbits are crepuscular and very social in their burrows or warrens, communicate through body language, and can show contentment and distress through actions like ‘binkies’ or thumping their feet.
The World of Rabbit Terminology
We begin by deciphering the terminology associated with rabbits. Did you know that a male rabbit is called a buck? And the female counterpart, a female rabbit is called a doe. Yes, just like deer! These terms are used across the rabbit world, from the smallest pet bunny to the largest European rabbit.
But what about the little ones, the baby rabbits? They are adorably referred to as kittens or kits. And when a doe has a family of kits from a single mating, we call that a litter. To address the parents of these kits, we use the terms dam for the mother and sire for the father.
Male Rabbits: The Buck Stops Here
Buck, the term used to refer to male rabbits, is quite fitting. Just like a dollar bill, bucks in the rabbit world hold a lot of value, especially when it comes to breeding.
Surprisingly, a buck retains its breeding capabilities up to about 7 years of age. That’s a lot of potential little kits!
Female Rabbits: Does It All
Shifting our focus to does, these female rabbits, also known as female rabbits, are the heart of the rabbit family, carrying and nurturing the next generation of happy rabbits.
Does reach sexual maturity and are ready to breed at just 5 to 6 months of age. They can continue to produce offspring for up to 4 years. That’s a lot of potential for little kits!
Rabbit Anatomy and Features
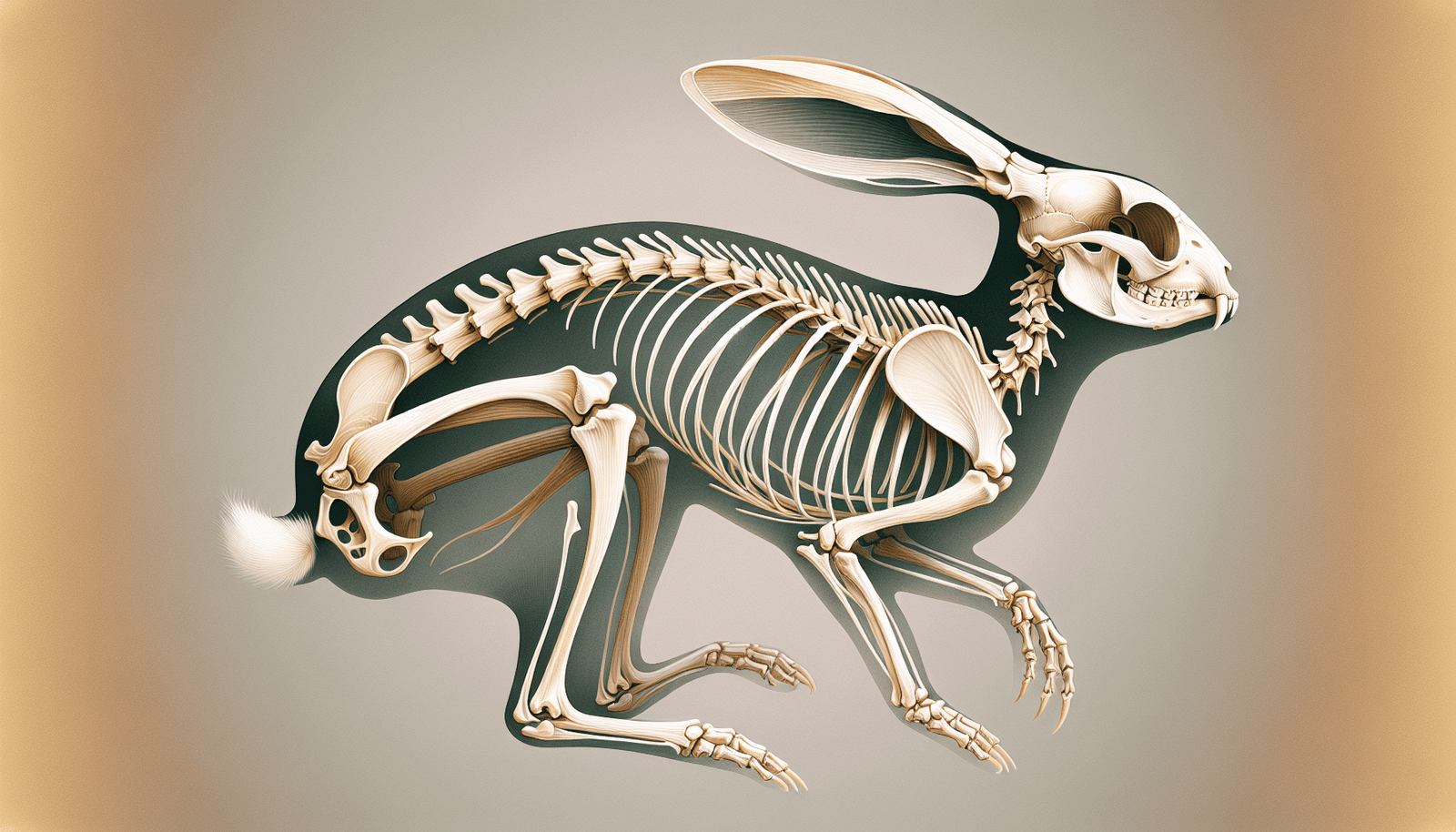
Beyond their cute and fluffy appearance, rabbits possess fascinating anatomy and distinct features. For starters, did you know that a rabbit’s skeleton is incredibly lightweight, making up only 8% of its total body weight? That’s even lighter than a cat’s skeleton!
Their spinal column is an intricate structure consisting of 46 bones segmented into various regions. They also have continuously growing teeth, which they wear down by munching on grass, hay, and leafy plants.
Ears: More Than Just for Listening
Rabbit ears, known as auricles or pinnae, are not just for detecting the faintest sounds. They also play a crucial role in temperature regulation. In warmer climates, these large, vascularized ears help rabbits disperse heat, keeping them cool and comfortable.
So, when you next encounter a rabbit, keep in mind that its long ears serve a vital function in thermoregulation, and aren’t merely for hearing or aesthetic appeal, but also help them detect predators and avoid actions that could attract predators.
Hind Legs: Built for Speed
Rabbits are known for their speed and agility, and their hind legs play a major role in this. They are structurally adapted for speed, with the tibia and fibula being longer than their forelegs, enhancing their hopping capability.
Additionally, rabbits employ digital locomotion – they move on their toes for an optimal stride. Their hind feet have four long, webbed toes, preventing spreading during hopping and aiding in forceful propulsion. This design collectively enhances a rabbit’s ability to produce faster speeds when hopping.
Understanding Rabbit Behavior
The diverse range of behaviors exhibited by rabbits makes them quite intriguing. They are crepuscular, meaning they are most active at dawn and dusk, which is when they typically graze. This is also the time when rabbits live their most social and active lives.
Their behaviors can also signal their emotions. For instance, a rabbit performing a ‘binky’ is expressing happiness, while flicking its feet after handling shows displeasure.
Social Groups and Warrens
Being social animals, some rabbits form intricate social structures within their network of burrows, referred to as warrens. These social groups provide various benefits, including safety from predators and shared resources.
Interestingly, while they are social, male rabbits, or bucks, are often housed separately to prevent fighting and manage breeding.
Body Language and Communication
Rabbits communicate in many ways, including through body language. For example, they use the position of their ears, tail, nose, and body posture to communicate with each other and humans. They also use full-body actions like flopping to express emotions.
Did you know that a rabbit thumping its hind feet on the ground is its way of signaling a threat or warning other rabbits of potential dangers near their territory?
Rabbit Reproduction and Offspring
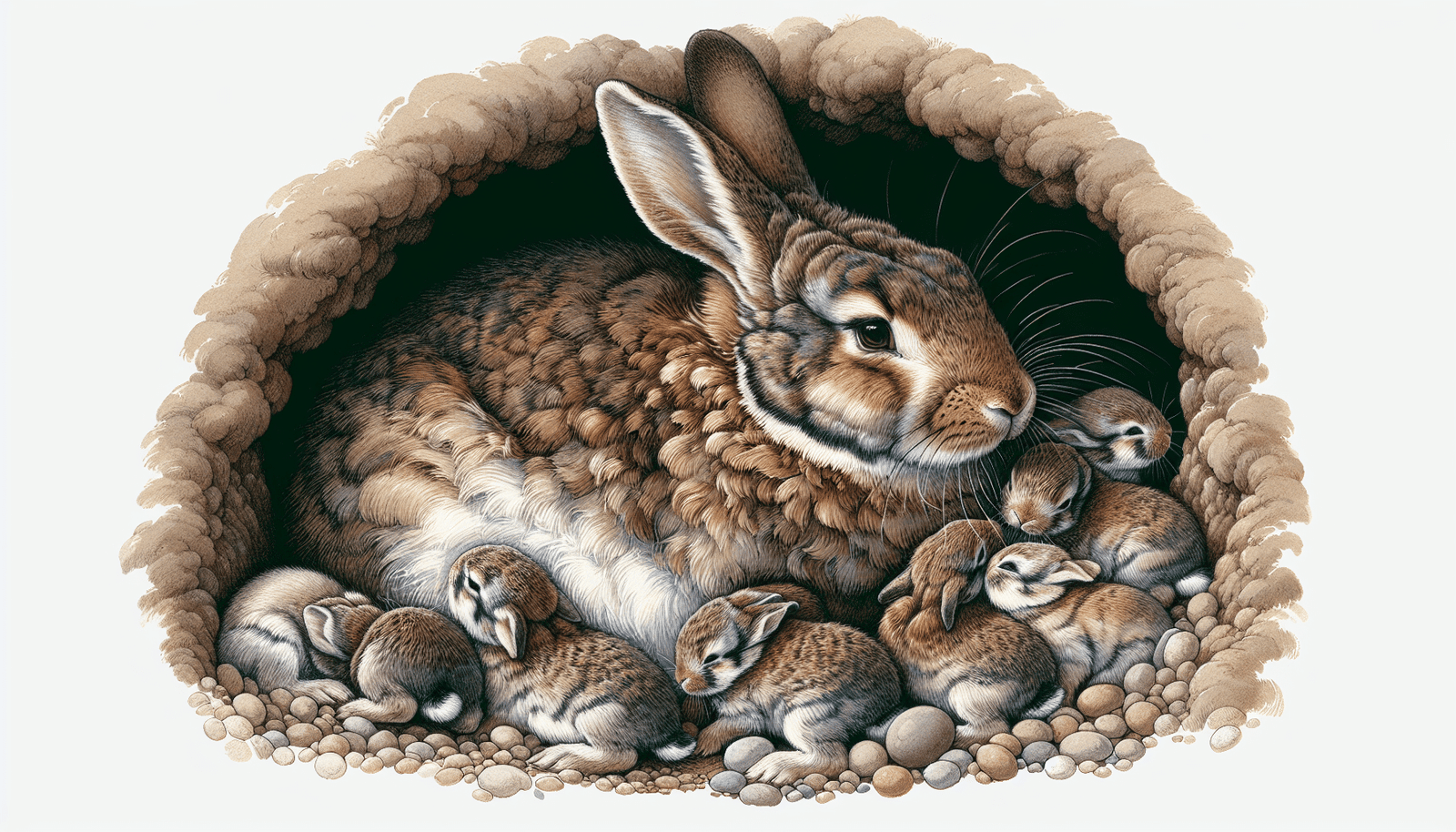
Rabbit reproduction is another fascinating aspect of these creatures. Female rabbits are induced ovulators, meaning they release eggs only after mating. Their pregnancy lasts for about 31 days, and they can give birth to anywhere from 1 to 12 kits.
Notably, two weeks post-mating, the developing kits can be felt through the side of a doe’s belly. Another interesting fact is that does can conceive again on the same day they give birth.
Baby Rabbits: Kits or Kittens?
Baby rabbits, whether you prefer to call them kits or kittens, are just as intriguing as their adult counterparts. These little ones, each a baby rabbit, are born into a world full of wonder and quickly start to explore their surroundings, bringing a new level of excitement to the rabbit world.
Rabbit Mating and Pregnancy
The rabbit mating process usually entails taking the doe to the place of the buck for copulation, after which the doe is returned to her own space.
Interestingly, rabbit females, or does, can accept males, or bucks, at any time of the year as they do not have a specific mating season.
Domestic Rabbits vs Wild Rabbits
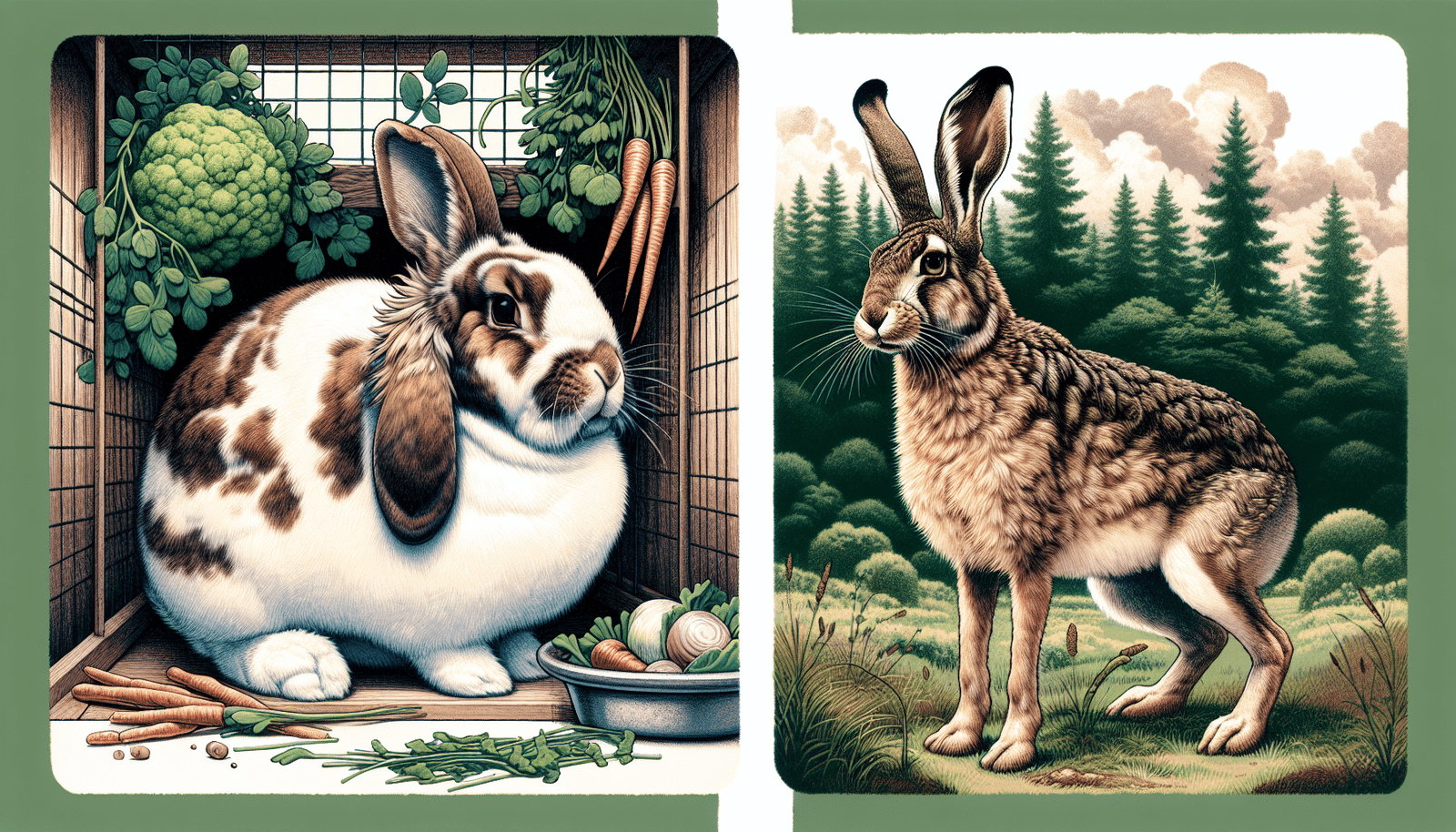
Significant differences exist between domestic rabbits and their wild counterparts. With nearly 50 breeds of domestic rabbits, contrasting with wild species like the Eastern cottontail, the rabbit world is more diverse than you might think.
Both domestic and wild rabbits, regardless of gender, establish territory through scent-marking. They rub their chins on objects to mark their possession using the scent gland located underneath their chin.
Domestic Rabbit Breeds
Domestic rabbits, including adult rabbits, come in a wide variety of breeds, each with its unique characteristics. Discovering rabbit facts can help you better understand and appreciate these fascinating animals.
From small to large breeds like the Flemish giants, domestic rabbits have been selectively bred for generations, making them dependent on human care and unable to survive independently in the wild.
Wild Rabbit Species
Wild rabbits, on the other hand, are a different story altogether. They are native to various parts of the world, with more than half of the world’s rabbit population residing in North America.
The Eastern cottontail, a wild rabbit species, is found in southern Ontario and is adapted to live outdoors without undergoing domestication.
Rabbits in Culture and Folklore
Rabbits have had a significant impact on culture and folklore, representing everything from the cycles of the moon to fertility, longevity, and rebirth.
From the White Rabbit in Alice in Wonderland to Beatrix Potter’s Peter Rabbit, these creatures have influenced our view of rabbits and continue to hold a special place in our hearts.
Caring for Your Rabbit: Diet and Health
Proper rabbit care demands a thorough understanding of their dietary requirements and potential health issues. A healthy rabbit diet primarily includes fresh, clean water, high-quality hay, and grass.
Rabbits also need daily exercise and should not be confined to small cages, as adequate space is vital for their well-being.
Dietary Needs and Feeding Tips
Rabbits absorb nutrients from their feed through their digestive tract. Leafy green vegetables, herbs, and weeds should be included in a rabbit’s daily diet to ensure they receive the necessary nutrients. Keep in mind that abrupt changes in diet can adversely affect a rabbit’s health. Hence, any dietary modifications should be introduced gradually.
Common Rabbit Health Issues
Rabbits, like any other pet, can experience health issues. For instance, when rabbits grind their teeth loudly, it can be an indicator of pain, similar to a cat’s purr when in discomfort.
Also, a change in the rabbit’s eating and drinking habits can signal a severe illness that necessitates immediate veterinary care.
Summary
In this journey through the world of rabbits, we’ve uncovered fascinating facts about their terminology, anatomy, behavior, reproduction, and the differences between domestic and wild species. Whether you’re a rabbit owner or simply a rabbit enthusiast, understanding these creatures’ unique characteristics, needs, and behaviors can help foster a deeper appreciation and love for them.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a male rabbit called?
A male rabbit is called a buck. Simple as that!
What are baby rabbits called?
Baby rabbits are called kittens or kits. Hope that helps!
What do rabbits eat?
Rabbits primarily eat fresh, clean water, high-quality hay, and grass for a healthy diet. Make sure to provide these for your rabbit’s nutrition.
How do rabbits communicate?
Rabbits communicate through body language signals like ear position, tail movement, and body posture, both with other rabbits and with humans. This helps them convey their feelings and intentions effectively.
What is the difference between domestic and wild rabbits?
The main difference between domestic and wild rabbits is that domestic ones have been bred to be dependent on human care, while wild rabbits can survive independently in the wild. So, domestic rabbits have been selectively bred for generations, making them reliant on human care, while wild rabbits can manage on their own.



