Have you ever been captivated by the elegant and agile Belgian Hare, a unique breed of rabbit with a rich history and fascinating characteristics? In this blog post, we will take you on a journey through the origins, development, and current status of this remarkable breed, highlighting the importance of preservation and responsible breeding along the way. Discover the history of Belgian Hares and learn about their fascinating past.
Key Takeaways
Belgian Hares are a breed of domestic rabbit developed in 18th century Flanders, selectively bred for its unique form and fur.
Eastern Europe’s oversaturation of the breed shifted focus to other rabbits and products, leading to the Belgian Hare Boom in the 19th/20th century US.
Clubs & associations have popularized this intelligent & loving pet. Responsible breeding is essential for preserving it for future generations.
Origins of the Belgian Hare
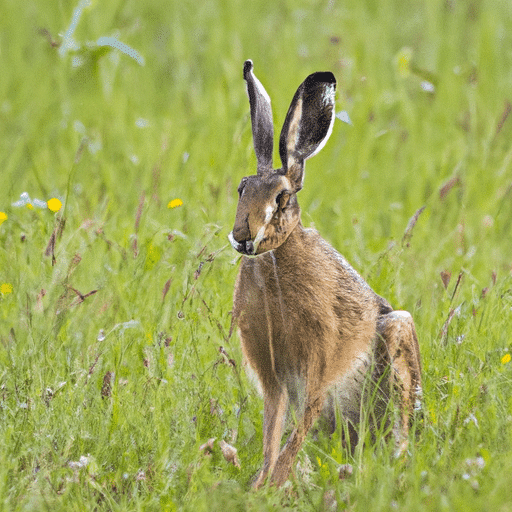
The first Belgian Hare breed finds its roots in the Flanders region of Belgium during the 18th century, where breeders set out to create a domestic rabbit breed that resembled the wild European hare in appearance and size, while also being suitable for meat production.
Development through Selective Breeding
Moving on to England in the 19th century, selective breeding was instrumental in defining the unique appearance of the Belgian Hare. The pioneering breeders, W.W. Lumb, Dr. J. Salter, and Dr. Barnham, sought to cultivate a rabbit with the form, color, and fur of the wild hare while also breeding for size. The first documented standards for this newly developed breed were established in 1882.
The Role of Eastern Europe
The evolution of the Belgian Hare was greatly influenced by Eastern Europe. Breeders in the Flanders area perfected the breed through selective breeding between domestic and wild European rabbits. This breeding process yielded the distinctive features of the Belgian Hare, such as:
its long head
straight tail
tall erect ears
deep red color with black waves or blotches on its sides
Eastern European rabbits’ introduction significantly transformed the rabbit breeding industry in Belgium. The impact of this introduction can be seen in the following ways:
The number of Belgian Hares experienced a considerable rise
This led to an oversaturated market for Belgian Hares
Subsequently, breeders and consumers shifted their focus to other rabbit breeds and products.
The Belgian Hare Boom in the United States

The Belgian Hare arrived in the United States in 1888, triggering a surge in popularity through the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The establishment of Belgian Hare clubs, which sought to promote the breed, precipitated the Belgian Hare Boom years, during which demand and prices rose sharply.
Formation of Clubs and Associations
In response to the breed’s popularity, various Belgian Hare clubs and associations were established, such as the inaugural National Belgian Hare Club of America. The National Pet Stock Association, which eventually became the American Rabbit Breeders Association, also played a role in the Belgian Hare’s recognition in the United States.
Founded in 1972, the American Belgian Hare Association has been instrumental in popularizing the breed in the US, boasting over 100 members across multiple states, Canada, and the UK. The formation of the American Belgian Hare Club, previously known as the National Belgian Hare of America Club in 1897, further contributed to the breed’s increasing popularity.
Impact on the Rabbit Breeding Industry
The surge in Belgian Hare’s popularity profoundly affected the US rabbit breeding industry. Substantial rabbitries were constructed specifically for Belgian Hare production, and the importation of thousands of Belgian Hares from 1898 to 1901 caused a dramatic rise in the breed’s fame and demand. The boom revolutionized the American rabbit breeding world and led to the establishment of standards for the Belgian Hare breed.
The Belgian Hare boom had substantial economic implications. Prices for quality breeding animals reached unprecedented heights, with a single buck being sold for an unparalleled price of $5000, equivalent to over $130,000 in today’s currency. However, the boom was short-lived, and the market eventually became saturated as the number of Belgian Hares multiplied exponentially, causing the rabbit breeding industry to redirect its focus to other breeds.
Physical Attributes and Characteristics
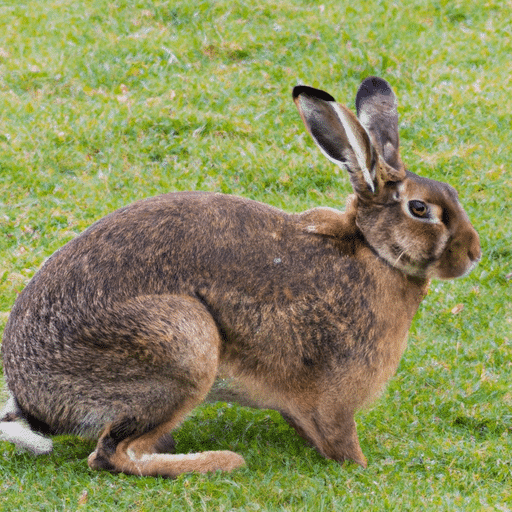

The Belgian Hare is distinguished from other rabbit breeds by its unique features, including a slender physique, an arched back, a long muscular flank, well-defined hindquarters, and longer limbs.
Its coat appearance is similar to that of a Wild Hare, exhibiting a red chestnut coloration with black ticking.
Comparison to Wild Hares and Other Rabbit Breeds
The Belgian Hare, also known as the Belgian Hare Rabbit, is a distinct breed of domestic rabbit. It has been selectively bred to resemble wild rabbits, particularly the wild European hare. Belgian Hare Rabbits are characterized by:
Their lithe and elegant body
Maximum weight of 9.5 lbs
Long head
Straight tail carried in line with the backbone
Tall, slightly wide, erect ears
A rich, brilliant, deep red of a tan or chestnut shade
The American Rabbit Breeders Association recognizes both the Rufous and Tan varieties of the Belgian Hare.
In comparison to other common domestic rabbit breeds, such as the Britannia Petite, Flemish Giant, Holland Lop, Mini Lop, Dutch, Netherland Dwarf, and Mini Rex, the Belgian Hare stands out in terms of its unique appearance and characteristics. Its features include:
Energetic and agile nature
Sleek and muscular body
Long and slender legs
Arched back
Alert and expressive eyes
These traits have earned it the nickname “rabbit racehorse”.
Uses and Applications of Belgian Hares
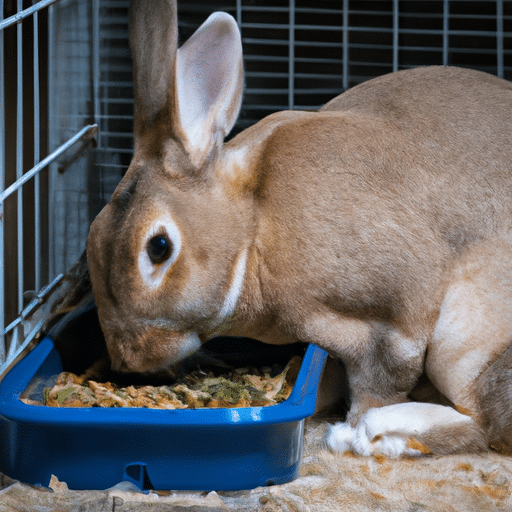

While initially bred for meat production, the Belgian Hare’s role has significantly evolved over time. Today, Belgian Hares are primarily bred as show rabbits or outdoor rabbits, and they are also known for their suitability as pets due to their intelligence and affectionate nature.
As a Meat Source
Historically, the Belgian Hare was created in the 18th century in the Flanders area of eastern Europe with the intention of producing a viable meat rabbit. Imported to England in 1874, it was mainly bred for its utility as a meat source. The Belgian Hare is known for its size and meat quality, making it a viable option for meat production.
Distinctive preparation methods for Belgian Hare meat include braising in Belgian ale and whole grain mustard, constructing hare terrine, and preparing hare a la Maryland. Despite its initial development for meat production, the Belgian Hare’s current uses extend beyond this purpose.
As Pets
Several characteristics make Belgian Hares ideal for pet ownership. They are renowned for their intelligence and can be readily trained, including litterbox training. Additionally, they are known to be affectionate companions and can learn their names. However, they are also highly sensitive and nervous, so they should be handled with caution.
Belgian Hares require a spacious outdoor enclosure that provides ample room for them to exercise and amuse themselves. It is advised that Belgian Hares receive at least an hour of exercise daily, as they are active and agile, and require sufficient space to move around and strengthen their hind legs.
Health Concerns and Care Requirements
Similar to other rabbits, Belgian Hares are prone to a range of health issues, including respiratory infections, ear mites, and various parasites.
Ensuring their overall health and well-being necessitates proper care, including a suitable environment, diet, and exercise.
Diet and Nutrition
Hay should make up 70% of the Belgian Hares’ diet, with the remaining 30% comprised of formulated rabbit food. Ensuring proper nutrition is crucial, as a lack of appropriate diet can lead to overgrown teeth, which can grow into the rabbit’s jaws and face, causing pain and hindering its ability to consume food.
Preventative measures for overgrown teeth include consuming hay, which helps to maintain healthy and properly worn teeth. Additionally, certain foods, such as iceberg lettuce, should be avoided in the diet of Belgian Hares.
Exercise and Mental Stimulation
It’s vital for the overall health of Belgian Hares to receive sufficient exercise and mental stimulation. Insufficient exercise may result in:
weight gain and obesity
health issues such as heart disease, diabetes, and joint problems
behavioral issues such as boredom, restlessness, and aggression.
Toys and activities that provide mental stimulation for Belgian Hares include:
Rough chew toys
Golf balls
Hardwood
PVC tubing
Toys that promote foraging and digging
These activities not only keep the Belgian Hare entertained but also contribute to its overall health and well-being.
Preservation Efforts and Current Status
The American Livestock Breeds Conservancy currently classifies the Belgian Hare breed as threatened. Preservation efforts include:
Dedicated fanciers worldwide striving to prevent the breed from extinction
Conservation efforts undertaken by organizations such as the Livestock Conservancy
Recognition and safeguarding of the breed in countries like the USA, UK, and across Europe.
Importance of Responsible Breeding
The health and longevity of the Belgian Hare breed greatly depend on responsible breeding. By guaranteeing the health, temperament, and genetic diversity of the breed, responsible breeders ensure that only healthy individuals with desirable traits are chosen for reproduction. This helps to avoid the propagation of genetic diseases and facilitates the overall health and vigor of the breed.
Irresponsible breeding can present various risks, such as:
a heightened risk of genetic defects in the offspring
a dearth of genetic diversity
contributing to pet overpopulation and inhumane treatment of animals
By adhering to responsible breeding practices, Belgian Hare breeders can help to preserve the Belgian Hare breed and ensure its continued existence for future generations.
Summary
In conclusion, the Belgian Hare is a remarkable and unique breed of rabbit with a rich history, captivating appearance, and fascinating characteristics. From its early development in the Flanders region of Belgium to its present-day status as a threatened breed, the Belgian Hare continues to captivate enthusiasts worldwide. By understanding the importance of responsible breeding and preservation efforts, we can ensure the survival of this elegant and historic breed for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the Belgian Hare?
The Belgian Hare is a domesticated breed of rabbit originally bred in Belgium in the 1800s for use as a meat animal. It has since become popular as a pet and for show purposes due to its spirited and lithe nature resembling that of wild European rabbits.
Are Belgian Hares rare?
Belgian Hares are indeed rare, due to dedicated fanciers worldwide striving to keep the breed from extinction and their distinct fur qualities which are lost when crossed with other breeds.
How long do Belgian Hares live?
Belgian Hares typically have a lifespan of 7-11 years, making them one of the longest-lived rabbit breeds.
How fast are Belgian Hares?
Belgian Hares are incredibly fast creatures, capable of reaching speeds of up to 30 mph and leaping 3 ft in the air.
Where did the Belgian Hare come from?
The Belgian Hare originated from Belgium in the early 18th century, through crossbreeding of domestic and wild European rabbits. This selective breeding was done with the intention of creating a practical meat rabbit for small livestock.



